Biology: Reproduction
Main Points:
|  |
Microscope:
A Microscope is an optical instrument having a magnifying lens or a combination of lenses for inspecting objects too small to be seen or too small to be seen distinctly and in detail by the unaided eye.
Cell Theory:
The Cell Theory is a theory formulated in the 1800's, the theory states that all living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of life, all cells come from other cells.
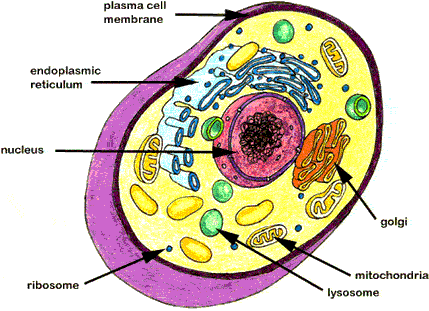
Structures of Cells:
Animal Cell
 | Plant Cell
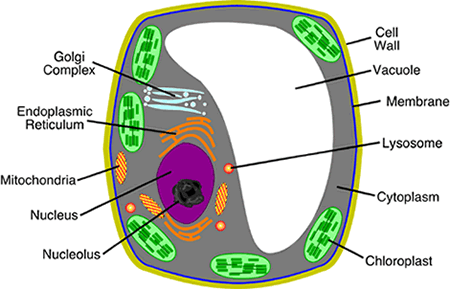 |
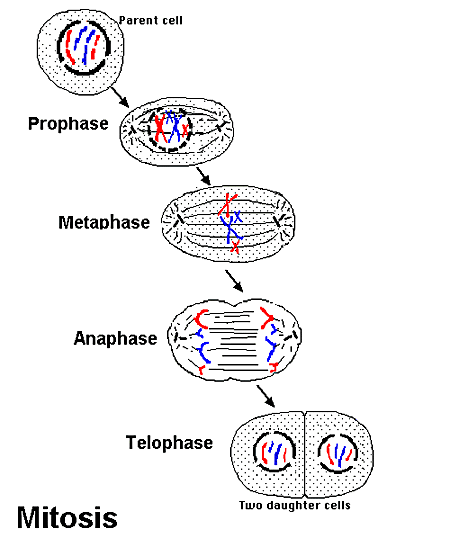
Cell Division - Mitosis:
Mitosis is the process by which genetic material duplicated divides into two identical sets of chromosomes.
Cancer:
Cancer is when a cell begins to divide uncontrollably. These cells continue dividing and pile up on top of one another. This will cause a bump or tumor. These cells can move to other parts of the organism. These cells gooble up oxygen and nutrients for themselves and robbing other cells food. Things like Tabacco, Asbestos, Certain Chemicals, Some Viruses, Radioactivity, and Ultraviolet radiation will increase ones chance of getting cancer.
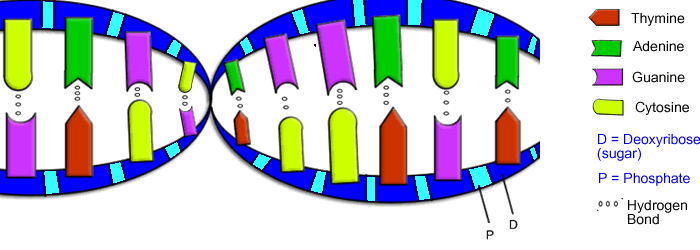
DNA Structure and Function:
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that determines the inherited characteristics of an organism.
Asexual Reproduction (budding, spores, fragmentation, binary fission):
Asexual Reproduction is the formation of a new individual from a single organism.
Budding- Budding is when a copy of the nucleus is made, then a tiny bud begins to form a new cell wall. That bud containing the new nucleus will continue to grow and will then break away creating a new cell.
Spores- A spore is a reproductive cell that can grow into a new individual through mitotic cell division.
Fragmentation- Fragmentation is when a small piece or fragment breaks away from the main mass of hyphae and grows into a new individual.
Binary Fission- Binary Fission is when a parent cell divides so that each new cell contains a single chromosome carrying a complete set of DNA identical to that of the parent.
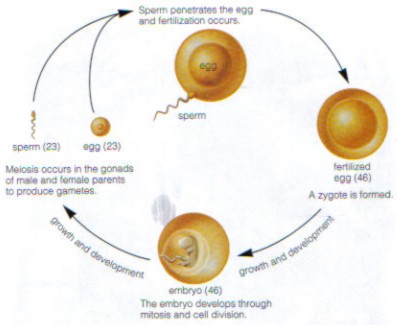
Sexual Reproduction in Animals:
Despite the differences among all animals, the fundamental sequence that allows them to reproduce sexually is the same.
- Meiosis produces gametes
- A male gamete (sperm) combines with a female gamete (egg)
- A zygote is produced and develops into an embryo
- The embryo develops through mitosis and cell division into a mature offspring.
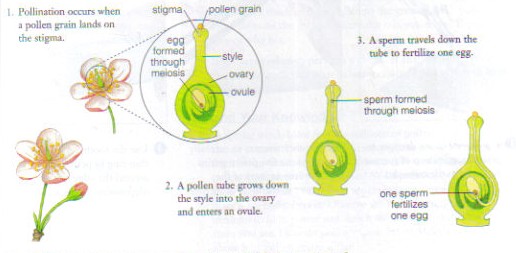
Sexual Reproduction of Plants:
- Meiosis produces gametes
- A male gamete (sperm) combines with a female gamete (egg)
- A zygote is produced and develops into an embryo
- The embryo develops through mitosis and cell division into a mature offspring.
Reproductive Strategies (i.e cloning):
Cloning- Is the process of producing a clone, a clone is an identical copy of a molecule, gene, cell, or entire organism.
Mutation- is a change in genes, produced by an error occuring during the process of copying DNA.
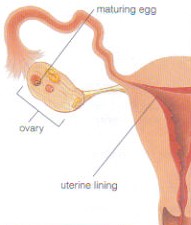
Formation of the Egg and Sperm Cells:
Egg Cells are produced inside of the ovary.
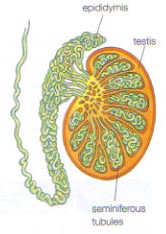
 | Sperm Cells are produced inside of the testes.
 |
Hormones and Reproductive Cycle:
Hormones- a substance released from specific glands to control particular body activities. Males have testosterone and females have estrogen and progesterone.
Reproductive Cycle
Female Reproductive Cycle
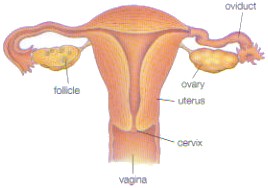 | Male Reproductive Cycle
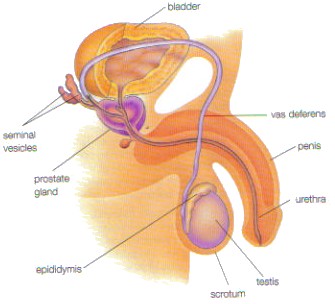 |
Karyotyping:
Karyotyping- is a photograph of a cell's chromosomes showing their arrangement fom largest to smallest.
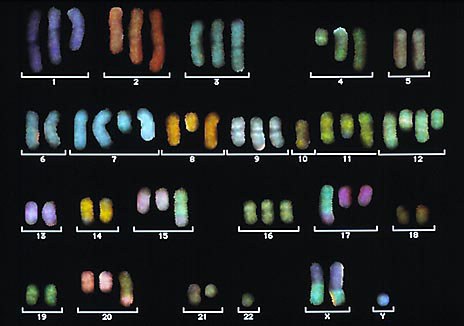
Genetic Screening:
Genetic Screening- is identifying human genetic conditions by examining the genes in an individual's cells.