Chemistry: Atoms and Elements
Main Points:
|  |
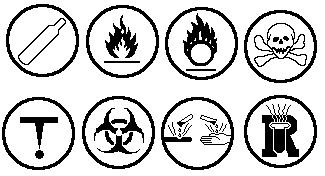
Safety Symbols
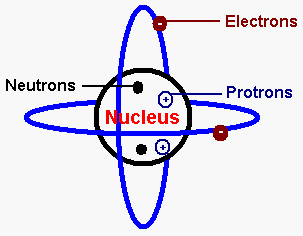
Particle Theory of Matter:
According to particle theory, all matter is composed of tiny particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. These tiny particles make up the atom. Atoms, ions and molecules are also particles.
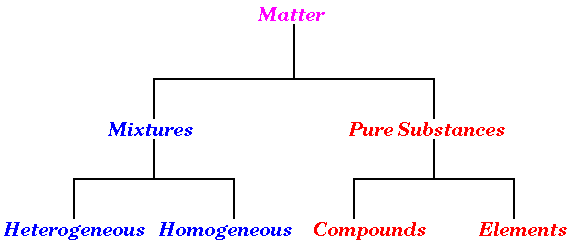
Classification of Matter:
Properties of Matter:
Any property that can be observed or measured without forming a new substance is a phsical property. Examples of Physical property are colour and density. Any property that describes how a substance reacts with another substance when forming a new substance is a chemical property. A example of a chemical property is combustibility.
Density / Metric Conversions:
Density- the amount of mass in a certain unit volume of a substance (density equals mass divided by volume.
Metric Conversions- Metric Conversions is the ability to convert different units of measurements.
Change in State:
Change in State- is when a solid, liquid, or gas will change from being a solid, liquid, or gas into a defferent state. Ex. Ice (solid) melting into water (liquid).

Changes of Matter:
Changes of Matter- With Changes of Matter, physical changes do not alter the composition of matter, when chemical cahnges will alter the composition of matter.
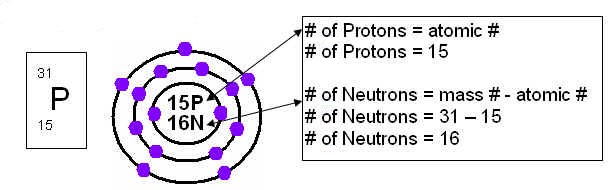
Subatomic Particles of the Atom:
Protons, Neutrons and Electrons are all examples of subatomic particles of the atom because they are smaller then the atom itself.
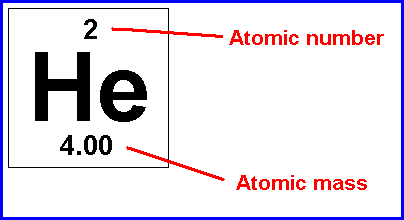
Atomic Number and Atomic Mass:
Atomic Number- is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Atomic Mass- is the mass of an average atom of an element, in atomic mass units.
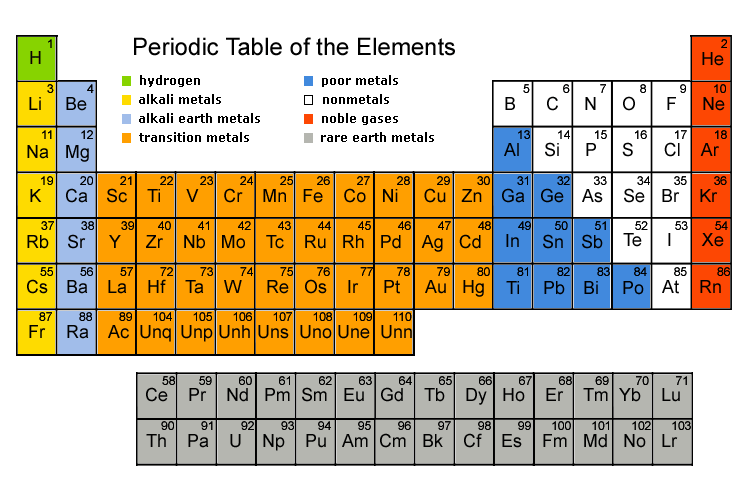
Metals and Non-Metals:
This is how Metals and Non-Metals fit in the Periodic Table of Elements.
Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams:
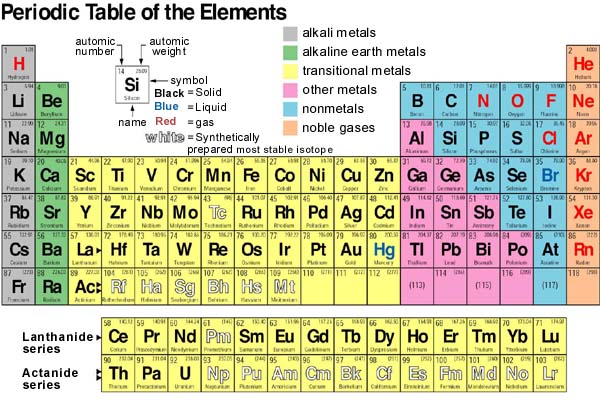
Trends of the Periodic Table:
There are many trends that can be found in the Periodic Table such as the ones seen in the table below:
Ionic Bonding:
Ionic Bonding- is the attraction between positive and negative ions.
Molecular Bonding:
Is the process in which two molecules are made into one.